The Printed Wiring Board (PWB) plays a vital role in modern electronics. It serves as the foundation for electronic circuits, providing a structured pathway for electrical connections. Though often mistaken for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), PWBs specifically refer to the base board before any components are mounted. Understanding the history, importance, and evolution of PWBs in electronics helps engineers, manufacturers, and tech enthusiasts appreciate their significance.
What is PWB?
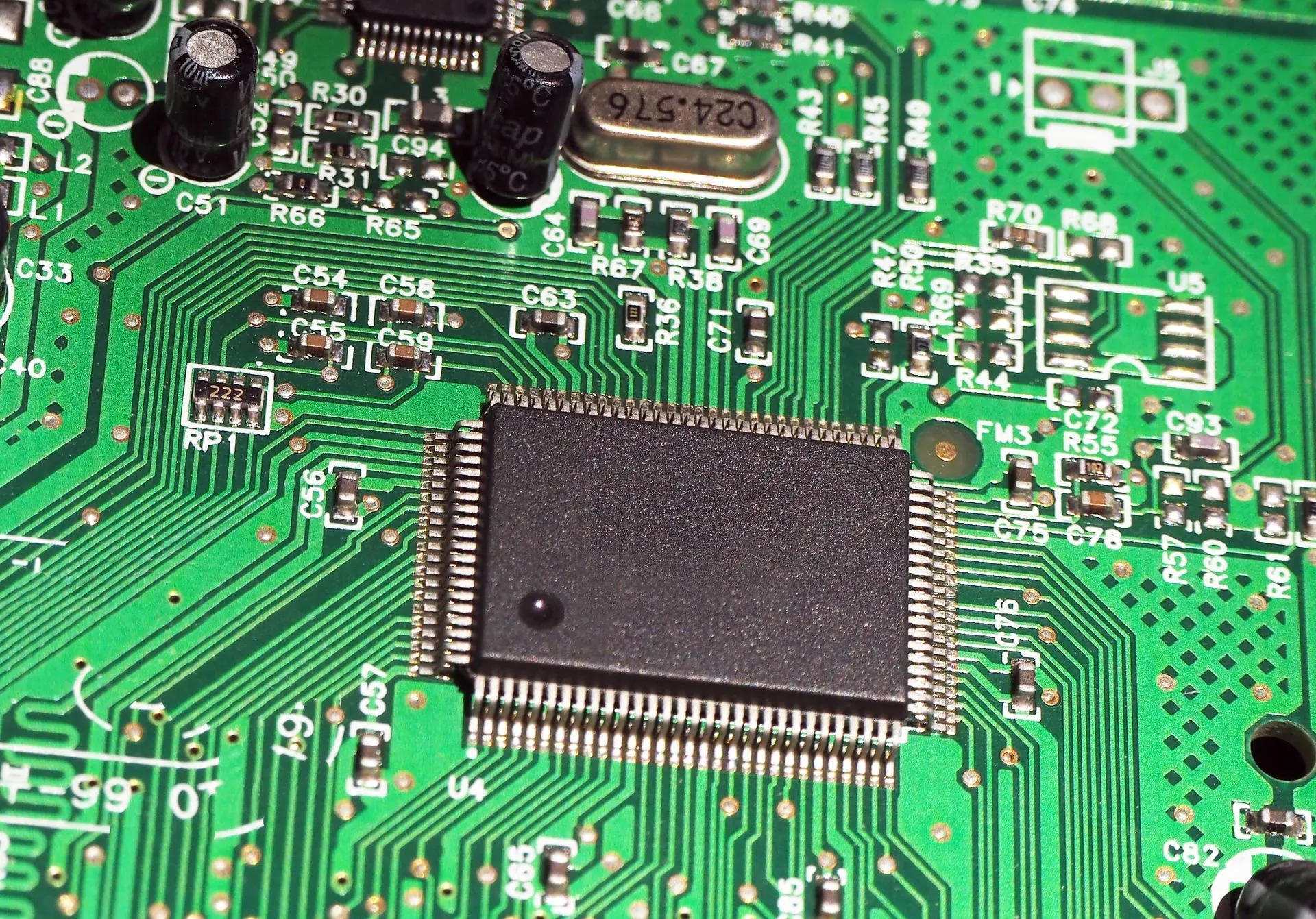
A Printed Wiring Board (PWB) is a flat, rigid, or flexible board made from materials like fiberglass or composite epoxy. It has thin layers of conductive pathways—usually copper—that guide electrical signals between different parts of an electronic circuit. Unlike PCBs, which already have mounted components like resistors and capacitors, a PWB refers only to the blank board with its conductive traces. It acts as the skeletal structure of an electronic device, ensuring a stable and organized connection between different components.
Evolution of PWB to PCB
The history of printed wiring boards dates back to the early 20th century when engineers needed an efficient alternative to bulky, point-to-point wiring systems. In the early days, circuits relied on complex and messy wiring, which made manufacturing difficult and prone to failures.
As technology evolved, PWB manufacturing processes improved, allowing conductive pathways to be etched directly onto rigid and flexible substrates. This change led to compact, reliable circuit designs. Over time, the term Printed Circuit Board (PCB) became the standard as assembly techniques improved and boards started coming with pre-mounted components.
PWB vs PCB: What’s the Difference?
A common question is the difference between PWB and PCB. While they may seem interchangeable, there’s a key distinction:
| Feature | PWB (Printed Wiring Board) | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) |
| Definition | A bare board with only conductive traces. | A complete board with mounted electronic components. |
| Components | No pre-mounted components. | Includes resistors, capacitors, ICs, etc. |
| Purpose | Used in prototyping and manufacturing before assembly. | Used in final electronic products. |
| Applications | Raw boards in electronic assembly factories. | Fully assembled circuit boards in consumer devices. |
Key Components of a Printed Wiring Board
A PWB circuit board is made up of several essential components that contribute to its function and reliability:
- Substrate (Base Material): This is the backbone of the board, commonly made of FR-4 fiberglass, ceramic, or flexible polymers.
- Copper Layer: Thin layers of copper form the conductive pathways for electrical signals.
- Solder Mask: This protective coating prevents accidental short circuits and makes soldering easier.
- Silkscreen Layer: The printed text and symbols that provide labels and markings for component placement.
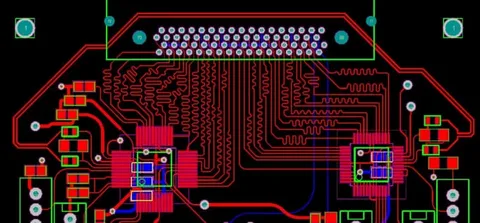
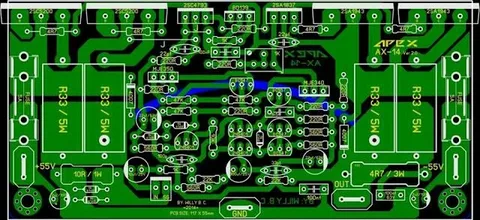
How PWB Design and Layout Optimization Works
Creating an efficient PWB layout involves careful planning to ensure proper signal flow and minimal interference. Engineers follow specific guidelines for:
- Component Placement: Arranging components for optimal performance and ease of assembly.
- Trace Routing: Designing paths that prevent electrical interference and signal loss.
- Thermal Management: Using heat sinks or thermal vias to dissipate heat efficiently.
- Multi-layer PWB Technology: Stacking multiple layers to handle complex circuit designs and reduce space requirements.
Applications of Printed Wiring Boards in Electronics
PWBs in electronic circuits are essential across a variety of industries. Some key applications include:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and smart appliances rely on high-density PWB technology to support their compact designs.
- Automotive Industry: Automotive printed wiring boards are used in vehicle control units, navigation systems, and sensor modules.
- Medical Devices: Medical instruments require high-frequency PWB designs for accurate readings and diagnostics.
- Industrial Automation: PWB technology in industrial automation ensures precise circuit control in automated machinery.
- Aerospace and Defense: Military-grade PWB circuit boards are designed to withstand extreme conditions and meet stringent reliability standards.
Choosing the Right PWB for Your Needs
If you’re selecting a Printed Wiring Board, here are key factors to consider:
- Material Type: Choose between rigid, flexible, or hybrid PWBs based on space and durability needs.
- Copper Thickness: Affects conductivity and heat dissipation—thicker copper improves durability.
- Layer Count: Single-layer PWBs are good for simple circuits, while multi-layer boards handle complex designs.
- Thermal & Electrical Properties: Ensure the board can handle expected temperature variations and maintain signal integrity.
The Future of PWB Technology
The future of Printed Wiring Board technology is constantly evolving. Some key advancements shaping the industry include:
- Flexible PWBs: Used in wearable devices, foldable phones, and medical implants.
- 3D Printed Wiring Boards: Revolutionizing prototyping and customized electronic designs.
- AI in PWB Design: Artificial intelligence is optimizing board layouts for better efficiency and reliability.
- Sustainable PWB Manufacturing: Companies are moving towards eco-friendly materials and waste-reduction techniques.
Conclusion
A Printed Wiring Board (PWB) is the foundation of modern electronics, providing a reliable medium for electrical connections in devices of all kinds. Understanding PWB manufacturing, PWB layout optimization, and PWB technology is essential for engineers, manufacturers, and anyone involved in circuit design. As the industry continues to evolve, advanced PWB design techniques and high-frequency PWB applications will keep driving innovation in electronics.