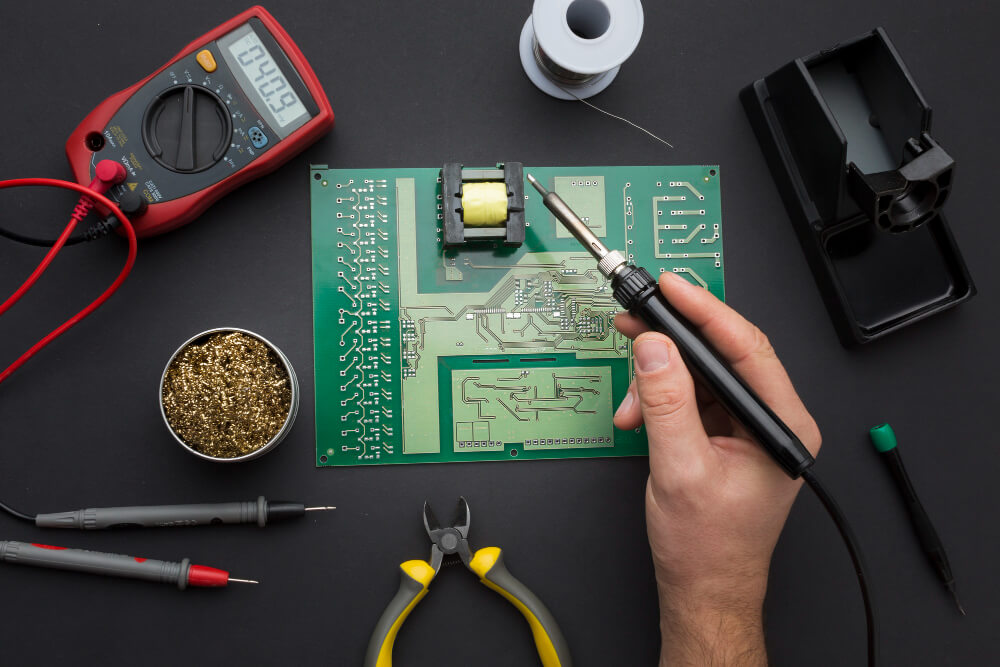
In recent years, LED lighting has transformed how we illuminate homes, businesses, and industrial spaces. Behind this innovation lies an essential backbone—PCB LED Lighting Assembly. This process integrates Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) into printed circuit boards (PCBs), enabling compact, efficient, and high-performance lighting systems.
Whether you’re in the electronics industry or simply curious about how your LED bulbs function, understanding PCB LED Lighting Assembly helps you appreciate the technology shaping modern lighting. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the complete process, materials, benefits, and applications of PCB LED assemblies.
What is PCB LED Lighting Assembly?
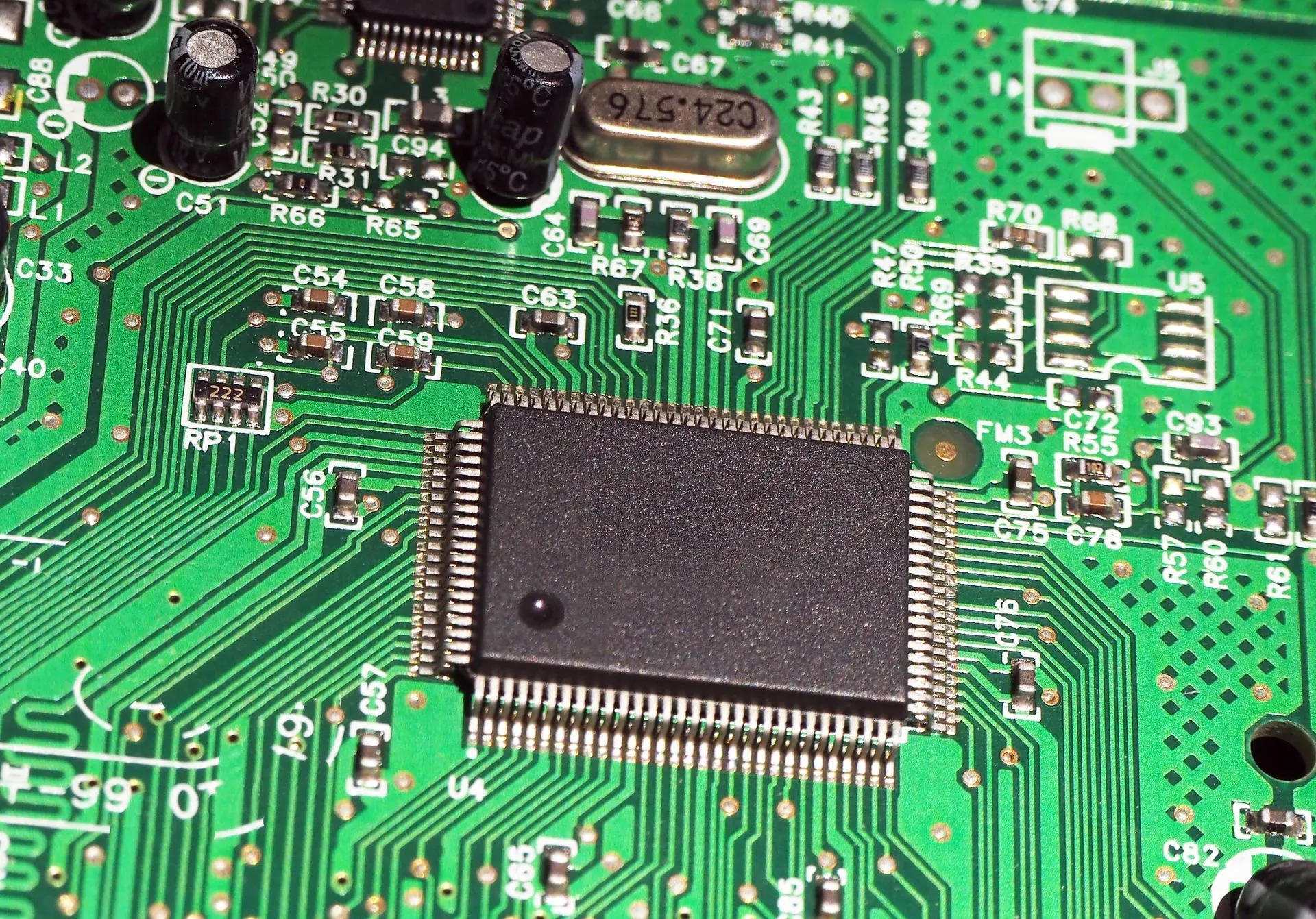
PCB LED Lighting Assembly is the process of mounting LED components onto printed circuit boards. These boards act as a platform to mechanically support and electrically connect LEDs using conductive pathways. The final product can be found in countless applications, from street lights and car headlights to televisions and mobile phones.
Unlike traditional lighting, LED PCB boards are highly customizable, energy-efficient, and built for long life spans. The quality of this assembly determines the performance, thermal efficiency, and durability of the LED system.
Key Components Involved in PCB LED Lighting Assembly
To fully grasp the process, it’s important to understand the components involved:
1. Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
The base of the LED lighting system. Materials range from FR-4 (fiberglass epoxy) for general use to aluminum PCBs for high-power applications due to their superior thermal management capabilities.
2. LED Chips
These are the primary light sources. Depending on the requirement, surface-mounted LEDs (SMDs) or high-power LEDs are used.
3. Heat Sink Layer
An essential part of any circuit board lighting setup, especially in high-power LED assemblies. This layer dissipates heat to ensure longevity and consistent performance.
4. Conductive Pathways
Copper traces connect all electronic components and are carefully designed to ensure efficient power flow and thermal control.
Types of PCBs Used in LED Assemblies
Different applications call for different types of PCBs. Below are the most commonly used varieties in PCB LED Lighting Assembly:
1. Aluminum PCB
Ideal for thermal management, aluminum PCBs are widely used in high-wattage lighting like street lamps and industrial floodlights.
2. Flexible PCB
Used in curved or dynamic lighting applications such as wearable tech or automotive interiors. These boards offer excellent adaptability.
3. Rigid PCB
A traditional option used in everyday lighting products such as household LED bulbs or LED strips.
4. Multilayer PCB
For more complex lighting assemblies with advanced features like dimming or programmable colors, multilayer PCBs are the best choice.
The Assembly Process of PCB LED Lighting
Let’s break down the LED assembly process step by step:
1. PCB Design
The process starts with a custom PCB layout, determining where LEDs, resistors, and traces will go. Attention to thermal design is critical here.
2. Material Selection
Depending on the heat and power requirements, materials like aluminum, FR-4, or ceramic substrates are chosen.
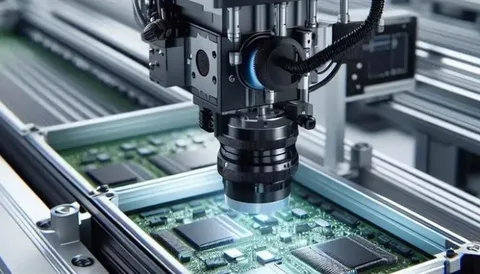
3. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Using surface mount technology, LEDs and other components are precisely placed onto the PCB with automated machines.
4. Soldering
The mounted components are soldered using a reflow oven or wave soldering process. Proper soldering ensures durability and electrical efficiency.
5. Thermal Management Testing
Once assembled, the board undergoes thermal cycling to test how well it handles heat. This is crucial to ensure heat dissipation is functioning properly.
6. Quality Assurance
Every board is visually inspected and electronically tested to ensure optimal functionality and safety.
Benefits of PCB LED Lighting Assembly
When done correctly, PCB LED Lighting Assembly offers numerous advantages:
1. Energy Efficiency
LEDs consume far less power than traditional bulbs, and with optimized circuit designs, the energy savings are maximized.
2. Compact Design
Using SMD components allows for ultra-compact and lightweight lighting systems.
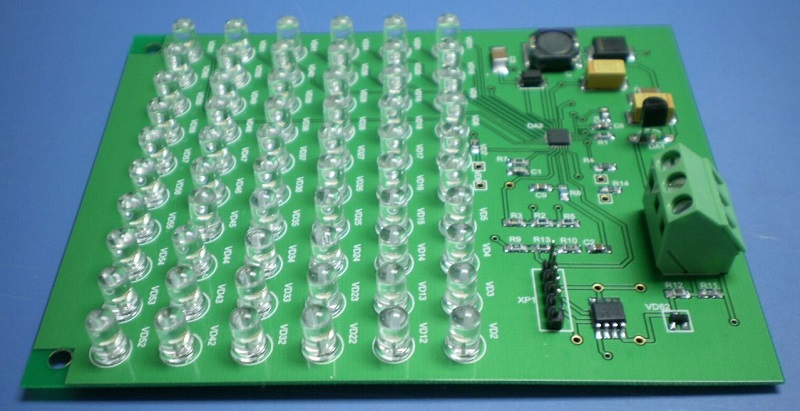
3. Longevity
Good thermal management and durable materials lead to extended product life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
4. Customization
From shape and size to color temperature and brightness, LED PCB boards can be tailored to specific needs.
5. Environmental Benefits
Reduced energy consumption and fewer material waste contribute to eco-friendlier lighting solutions.
Common Applications of PCB LED Assemblies
The versatility of PCB LED Lighting Assembly makes it suitable for a wide range of uses, including:
- Consumer Electronics: TVs, smartphones, laptops
- Automotive Lighting: Headlights, dashboard lights, ambient lighting
- Industrial Lighting: High-bay lights, machine lights
- Medical Devices: Surgical lamps, diagnostic equipment
- Architectural and Decorative Lighting: LED strips, backlit panels
- Street and Outdoor Lighting: Floodlights, solar-powered LEDs
Design Considerations for PCB LED Lighting Assembly
When designing an LED PCB, several factors must be taken into account to ensure reliability and efficiency:
1. Heat Dissipation
Using aluminum PCBs and incorporating heat sinks helps in spreading heat away from sensitive components.
2. Current Management
LEDs are current-sensitive. Circuits must be designed with proper resistors or constant current drivers to avoid failure.
3. Optical Output
PCB layout influences the direction and intensity of light. Reflectors or lenses may be used to enhance light quality.
4. Durability
Considerations like moisture protection and impact resistance are essential for outdoor or industrial use.
Challenges in PCB LED Lighting Assembly
Despite its advantages, some challenges must be addressed:
- Thermal Runaway: If heat is not managed, it can lead to device failure.
- Solder Joint Reliability: Poor soldering can cause flickering or total failure.
- Design Complexity: Custom designs can be expensive and require skilled engineering.
- Material Costs: High-quality substrates like ceramic or aluminum are costlier but necessary for performance.
Future Trends in PCB LED Lighting
As LED technology evolves, so does the complexity and capability of PCB assemblies. Here are a few trends shaping the future:
1. Smart Lighting Integration
Combining PCB LED Lighting Assembly with IoT allows remote control, automation, and energy monitoring.
2. Miniaturization
Smaller and more powerful components are allowing more compact and flexible lighting applications.
3. Sustainable Manufacturing
Eco-friendly materials and low-emission manufacturing processes are becoming industry standards.
4. Advanced Thermal Solutions
Innovations like graphene heat spreaders and nanotechnology promise to improve heat dissipation dramatically.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of PCB LED Lighting Assembly reveals the engineering marvel behind the LED lights we use daily. From board design and material selection to assembly and testing, each step plays a critical role in the final product’s performance and reliability.
Whether you’re an electronics manufacturer or a lighting enthusiast, investing in high-quality PCB LED lighting assembly ensures energy efficiency, long life, and superior performance. As demand for smarter, greener lighting grows, mastering this assembly process is more relevant than ever.